Busbars represent a cornerstone of modern electrical distribution systems, offering a highly efficient solution for power transmission in industrial and commercial applications. These robust conductors revolutionize power distribution by minimizing energy losses, reducing installation complexity, and providing superior thermal management compared to traditional cable systems while ensuring reliable electrical connectivity across diverse applications
Table of Contents
What are Busbars?


Busbars are electrical conductors that transfer and distribute power to multiple circuits, devices, or components within the electrical system. Generally, they act as a central path that can efficiently carry, transfer, and distribute large amounts of current to various circuits and components. They are typically a strip or bar of copper, aluminum, or another conductive material that serves as a common connection point in electrical systems.
What are Busbars made of?
Busbars are primarily manufactured from highly conductive metals, with copper and aluminum being the predominant materials of choice. Copper busbars offer superior electrical conductivity (approximately 100% IACS) and excellent thermal performance, while aluminum alternatives provide a cost-effective solution with approximately 61% conductivity compared to copper. These conductors are often enhanced with protective coatings such as tin, silver, or nickel plating to prevent oxidation and ensure optimal electrical contact. The selection of material composition depends on factors including current capacity requirements, environmental conditions, and economic considerations in the electrical distribution system design.
Top 6 Key Benefits of Using Busbars
Busbars offer significant technical and operational advantages in electrical power distribution, making them an optimal choice and efficient solution for various industrial and commercial applications. The following advantages demonstrate their superiority over traditional wiring methods:
1. Space Optimization
The compact design of busbar solutions can reduce space requirements by 30-40% compared to traditional cable installations. Therefore, this space efficiency is particularly valuable in applications such as data centers and industrial applications where space constraints are critical. Additionally, the systematic arrangement will allow for better air circulation and cooling.
2. Thermal Management
Due to the high surface-area-to-volume ratio; busbars exhibit superior heat dissipation properties. Thus, the enhanced thermal conductivity allows them to operate at lower temperatures than equivalent cable installations, typically maintaining temperatures 15-20°C lower under identical load conditions. This thermal efficiency extends component lifespan and reduces cooling requirements.
3. Safety and Reliability
Busbars solutions incorporate advanced insulation housing materials and protective features that significantly enhance operational safety and reduce the risk of short circuits. Moreover, the rigid construction and enclosed design minimize the risk of electrical faults, while standardized connection methods reduce the possibility of installation errors compared to traditional wiring methods. In conclusion, statistical analysis shows that properly maintained busbar solutions have a failure rate of approximately 75% lower than equivalent cables in traditional installations.
4. Increase the Electrical Efficiency
The cross-sectional area and the optimized geometry of busbars result in lower electrical resistance compared with conventional cables. This reduced resistance leads to minimal power losses in the electrical circuits through heat dissipation, typically achieving efficiency rates up to 99% in modern systems where even small losses can result in significant energy waste. The consistent impedance characteristics also help maintain stable voltage levels throughout the distribution network in the electrical systems.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
While initial installation costs may be higher, the total cost of Rolinx busbars solutions is typically 20-30% lower over a 10-year period when considering:
- Reduced maintenance requirements.
- Lower power losses.
- Decreased cooling needs.
- Extended system lifespan.
- Minimal downtime during modifications.
6. Maintenance, Installation, and Flexibility
Busbar solutions feature modular designs that facilitate maintenance and system modifications. Furthermore, simplify electrical connections by reducing the number of required individual cables. For this reason, connection points can be accessed without disrupting the entire system, reducing mean time to repair (MTTR) by up to 60% compared to conventional wiring. The standardized connection interfaces also enable rapid system reconfiguration and expansion.
Therefore, these advantages make busbar solutions an essential component in modern electrical distribution systems, particularly in applications requiring high reliability, efficiency, and adaptability.
Busbars vs Cables
| Aspects | Busbars | Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Current Carrying Capacity | ● Higher current density capability (up to 6A/mm²) ● Enhanced heat dissipation through a larger surface area ● Lower temperature rise under maximum load conditions ● Optimal performance in high-current applications (>800A) | ● Lower current density (typically 2.5-4A/mm²) ● Limited by conductor and insulation thermal properties ● Temperature-dependent performance ● Suitable for lower current applications (<800A) |
| Physical Properties | ● Rigid copper or aluminum conductors ● Standardized cross-sections ● Typical thickness range: 5-12mm ● Available in various plating options (tin, silver, nickel) | ● Flexible stranded conductors ● Circular cross-section ● Multiple insulation layers ● Various conductor materials (copper, aluminum) |
| Installation Characteristics | ● Modular assembly system ● Fixed routing paths ● Bolted or welded connections ● Lower voltage drop across joints (0.1-0.2%) | ● Flexible routing options ● Multiple termination methods ● Crimp or compression fittings ● Higher voltage drop at terminals (0.3-0.5%) |
| Thermal Performance | ● Operating temperature: up to 85°C ● Superior heat dissipation coefficient ● Lower thermal resistance ● Better short-circuit thermal stability | ● Operating temperature: up to 70°C (PVC) or 90°C (XLPE) ● Limited by insulation properties ● Higher thermal resistance ● Requires derating in bundles |
| Space Utilization | ● Space factor: 1.2-1.5 ● Vertical stacking possible ● Compact parallel arrangements ● Reduced clearance requirements | ● Space factor: 2.0-2.5 ● Requires cable management systems ● Limited by minimum bending radius ● Additional space for heat dissipation |
| Maintenance Requirements | ● Inspection interval: 2-3 years ● Visual inspection capability ● Minimal connection maintenance ● Lower oxidation risk with proper plating | ● Inspection interval: 1-2 years ● Regular termination checks required ● Insulation testing needed ● Higher risk of insulation degradation |
| Economic Aspects | ● Higher initial investment ● Operational lifespan: 25-30 years ● Lower maintenance costs ● Better long-term ROI | ● Lower initial cost ● Operational lifespan: 15-20 years ● Higher maintenance expenses ● More frequent replacement needs |
Pros and Cons: Busbars vs Cables
Busbars Pros and Cons
| BUSBARS Pros | BUSBARS Cons |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Thermal Management ● Superior heat dissipation due to a larger surface area ● Lower operating temperatures under high current loads ● Reduced thermal stress on connections and joints | Initial Investment ● Higher upfront cots at the beginning ● Specialized installation expertise required ● Additional planning and design considerations |
| Space Optimization ● Compact installation footprint compared to equivalent cable systems ● Ertical stacking capabilities ● More efficient use of limited space in electrical rooms | Limited Flexibility ● Fixed routing paths once installed ● Challenging to modify after installation ● Limited bending and turning capabilities |
| Maintenance Efficiency ● Easy visual inspection of connections ● Implified maintenance procedures ● Reduced need for periodic retightening of connections | Specialized Skills Required ● Specific training needed for installation ● Fewer qualified installers available ● Higher labor costs for specialized work |
| Current Carrying Capacity ● Higher ampacity per cross-sectional area ● More efficient power distribution ● Better performance in high-current applications | |
| Long-Term Cost Effectiveness ● Extended operational lifespan (typically 25-30 years) ● Lower maintenance requirements ● Reduced material replacement costs | |
| Installation Advantages ● Modular design for easy expansion ● Faster installation time ● Fewer connection points required |
Cables Pros and Cons
| CABLES Pros | CABLES Cons |
|---|---|
| Installation Flexibility ● Easily routed around obstacles ● Suitable for complex pathway requirements ● Adaptable to various installation configurations | Space Requirements ● A larger installation footprint needed ● Complex cable management systems required ● Challenging in confined spaces |
| Initial Cost Efficiency ● Lower upfront material costs ● Reduced initial installation expenses ● More economical for smaller projects | Maintenance Issues ● Regular inspection of connections required ● Potential degradation of insulation ● More frequent maintenance intervals |
| Widespread Availability ● Ready availability of materials ● Multiple supplier options ● Standard sizes and specifications | Thermal Limitations ● Lower heat dissipation capacity ● Reduced performance at high currents ● More susceptible to thermal aging |
| Familiarity ● Well-understood installation methods ● Widely trained workforce ● Established industry standards | Long-term Cost Implications ● Higher maintenance costs over time ● More frequent replacement needs ● Increased labor costs for modifications |
What are the ROLINX Laminated Busbars?
Laminated busbars from Rolinx are high-performance electrical conductivity solutions designed for efficient power transmission and distribution in complex electrical systems. These precision-engineered components represent a sophisticated approach to electrical interconnection and power management. Therefore, the laminated busbars are considered advanced power distribution technology.


ROLINX Laminated Busbars vs Traditional Busbars
Electrical power transmission technologies have undergone significant evolutionary transformations, with laminated busbars emerging as a sophisticated alternative to traditional busbar configurations. This comparison explores the critical distinctions between these two power distribution methodologies.
| Aspects | ROLINX LAMINATED BUSBARS | TRADITIONAL BUSBARS |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Composition and Design | Multi-layered precision-engineered structures Complex, customizable geometric configurations Advanced material stratification Integrated insulation and conductive layers Enhanced dimensional precision | Typically, single-layer metallic conductors Conventional rectangular or flat bar configurations Limited geometric flexibility Basic material composition (primarily copper or aluminum) |
| Current Capacity and Efficiency | Optimized current distribution through engineered layering, significantly reduced electrical resistance | Linear current transmission with inherent resistance limitations |
| Electromagnetic Interference Management | Advanced electromagnetic interference management shielding through strategic material selection and layering techniques | Minimal electromagnetic interference management suppression capabilities |
| Thermal Management | ● Sophisticated thermal dissipation architecture ● Integrated thermal management layers ● Consistent performance across extensive temperature ranges ● Reduced thermal stress on electrical systems | ● Basic heat dissipation mechanisms ● Limited thermal stability ● Potential performance degradation under high-temperature conditions |
| Mechanical Integrity | ● Enhanced structural strength ● Superior vibration resistance ● Improved dimensional stability ● Customizable mechanical characteristics | ● Standard mechanical properties ● Susceptibility to vibration-induced structural fatigue ● Limited mechanical resilience |
| Application Domain Suitability | ● Electric vehicle power systems ● Advanced renewable energy infrastructure ● High-precision electronic equipment ● Battery management technologies ● Aerospace and automotive engineering ● Sophisticated telecommunications networks | ● Conventional industrial electrical systems ● Legacy power distribution infrastructure ● Limited high-performance applications |
| Cost and Manufacturing Considerations | ● Advanced manufacturing technologies ● Higher initial production complexity ● Precision engineering requirements ● Customization-oriented design approach ● Long-term performance optimization | ● Lower initial manufacturing complexity ● Standardized production processes ● Limited customization potential ● Reduced per-unit manufacturing costs |
| Performance Metrics | ● Current Efficiency: High ● Thermal Stability: Superior ● EMI Suppression: Excellent ● Mechanical Resilience: Advanced ● Design Flexibility: Extensive | ● Current Efficiency: Moderate ● Thermal Stability: Limited ● EMI Suppression: Minimal ● Mechanical Resilience: Standard ● Design Flexibility: Restricted |
Types of ROLINX Laminated Busbars
ROLINX Easy
Designed for low and medium-voltage applications with lower electrical performance requirements. ROLINX Easy laminated busbar solution is without outer insulation and closed mold technology, offering high short circuit resistance, optimized conductivity, and high currents above 1000A.
- High short circuit resistance and low conductivity.
- A cost-effective alternative for stacked busbars.
- Manufactured in a controlled production process.
- The ease of use helps to reduce installation times.


ROLINX Performance
Designed for medium and high voltage applications and in combination with high currents over 1000A. ROLINX Performance laminated busbar offers all material, lamination, and plating configurations with optimized inductance and design to control partial discharge.
- Provides optimized inductance.
- Designed for controlling partial discharge
- Shaped to fit high-voltage applications
- Proven technology


ROLINX Thermal
An evolution of ROLINX Performance offering increased working temperature up to 130°C.
- Developed to get more power from the existing system and design.
- Extended thermal characteristics: up to 130°C.
- Extended humidity rating.
- Designed to last.


ROLINX Hybrid
One piece solution combines power and signal lines. ROLINX Hybrid laminated busbar is for low-voltage applications like battery cell connection in Electrical Vehicles.
- One-piece solution for signal lines and power connection in battery modules.
- Reduces installation time.
- Eliminates wiring errors.
- Streamlines the supply chain.


ROLINX Power-Circuit
Designed as an alternative solution to traditional PCBs. It offers high voltage and current capacity with low inductance and compact 3D design.
- Compact 3D design.
- Fit for high-volume assembly processes.
- Good thermal management.
- Low inductance.
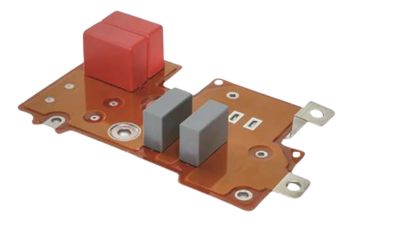

ROLINX Compact
Busbar uses epoxy powder coating as outer insulation instead of insulation films. It offers tight-fitting solutions when limited space is available.
- Optimized design fit for narrow space connection.
- High power density capabilities.
- High-temperature resistance.
- Easy to insulate very complex shapes.


ROLINX Flex
Flexible busbars are pure copper laminates within protective PVC insulation offering flexibility for customized solutions.
- Flexible configurations with/without rigid parts.
- Easy and quick bending.
- Ideal for parts with vibrations and/or thermal expansion.
- Space saving in compact designs.
- Design flexibility.


ROLINX Housing Solutions
Injection molded solutions in combination with busbars offer great flexibility for customized solutions.
- Integration of connectors or structural functions.
- Reduced weight.
- Space savings in compact designs no spacers required.
- Improves design flexibility with complex 3D shapes.
- Ideal for high-volume production.


ROLINX CapLink Solutions
Capacitors integrated on ROLINX Laminated Busbar Solutions offer a low inductance.
- Low ESL & ESR.
- High ripple current capabilities.
- High reliability.
- Long useful life.


ROLINX Busbars Engineering Services
Include a range of services to meet critical application needs regardless of size or complexity. Our services include current, heating, and inductance simulations, and standard and specific testing capabilities like static self-heating and accelerating aging tests.
- Increased reliability due to the optimized busbar layout.
- Reduced busbar architecture complexity.
- Minimized design risk and costs.
- Increased flexibility.
- Lower total cost of ownership.
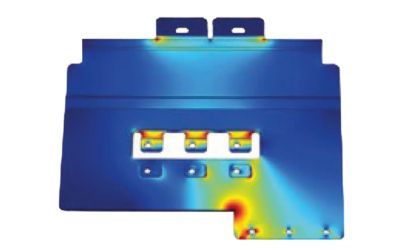

ROLINX Busbars Electrical Parameters
Current
Typical range: 100A – 2000A
Voltage
The busbars can operate at different DC voltage levels. Typical values for nominal, rated insulation, impulse withstand, high potential, and partial discharge voltages are listed below and are determined according to EN 50124-1 chapter 4.2.3.1 Annex D table D.1 are the following:
| Typical nominal DC voltage (V) | Rated insulation voltage Ui (V)* | Rated impulse withstand voltages Uimp (kV) OV2 |
|---|---|---|
| 750 | 900 | 5 |
| 1500 | 1800 | 8 |
| 3000 | 3600 | 12 |
- *Minimum nominal +20% depending on application (higher relative percentage for the railway power distribution systems)
- The high voltage test can be determined as per the formula: 2*Ui+2kV acc. IEC 60077 Annex B.3 during 1 minute.
- To determine partial discharge voltage see point Partial Discharge.
Clearance Distance
Clearance is the shortest distance in air between two conductive parts. Typical clearance values according to EN 50124-1 chapter 5.2 table A.3 and overvoltage category 2 (OV2) are the following:
| Typical nominal DC voltage (V) | Rated impulse withstand voltages Uimp (kV) 1.2 / 50µs | Minimum clearance distance in air (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 750 | 5 | 4 |
| 1500 | 8 | 8 |
| 3000 | 12 | 14 |
Overvoltage category OV2 definition: Circuits that are not directly connected to the contact line, and which are protected against over-voltages.
Creepage Distance
Creepage distance means the shortest distance along the surface of a solid insulating material between two conductive parts. Typical creepage values according to EN 50124-1 chapter 6.2 table A.7 and insulation materials group 1 (CTI <600V 5mm / kV) and pollution degree 2 (PD2) are the following:
| Typical nominal DC voltage (V) | Rated insulation voltage Ui (V)* | Creepage distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 750 | 900 | 4.5 |
| 1500 | 1800 | 9 |
| 3000 | 3600 | 18 |
- *Minimum nominal +20% depending on application (higher relative percentage for the railway power distribution systems)
- Pollution degree PD2 definition: Normally only non-conductive pollution occurs. Occasionally, however, a temporary conductivity caused by condensation is to be expected when the equipment is out of operation.
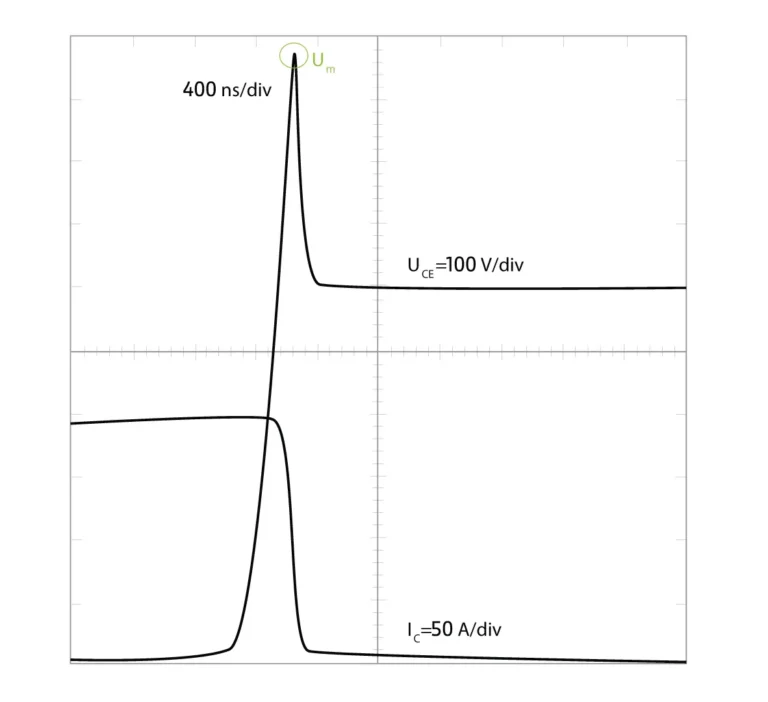
Partial Discharge
The partial discharge test helps to predict the future performance and reliability of the busbar. Typically partial discharge should be below <10pC according to IEC 61287 at defined voltage Vtest.
- Vtest= 1.1 Um /√2
- Um: maximum repetitive commutation voltage at max DC voltage
- Convert to rms (/√2) root mean square
- 10% extra margin

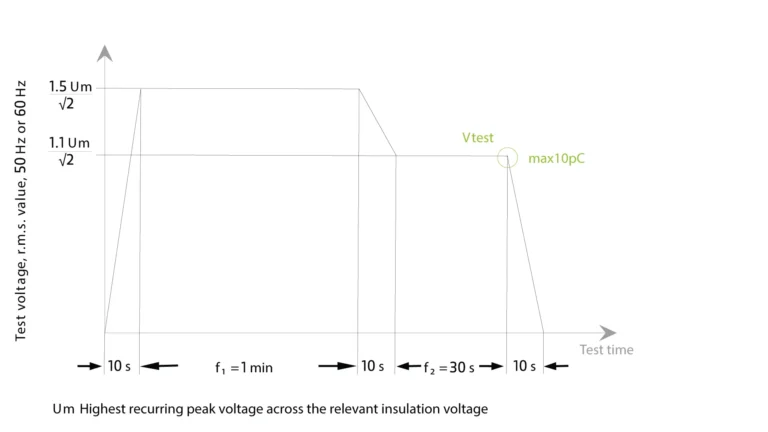
Test Cycle:
- 1min 1.5 Um / √2
- 30s Vtest 1.1 Um / √2
- Max 10pC @ last 5 s Vtest



ROLINX Busbars Mechanical Parameters
Physical Dimensions and Tolerances
The table below lists the physical dimensions and standard tolerances for the busbars.
| Dimension | Standard tolerance |
|---|---|
| Tolerance on holes | +/- 0.05mm |
| Distance distances | +/- 0.2mm |
| Sub assembly | +/- 0.6mm |
| Angle | +/- 1° |
ROLINX Busbars Features
There are various features to terminate the busbar for system connection. The table below describes the most common methods and some factors to be considered when designing a busbar.
| Connection | Typical current values |
|---|---|
| Bushing | > 100A |
| Dishing (up to 2mm conductor) | > 50A |
| Star dishing (up to 3mm conductor) | > 50A |
| Solder pin | < 10A |
| Faston tab | < 20A |
| Fastened threaded stud | > 100A |
| Fastened screw | > 100A |
| Connectors | As per request |
ROLINX Busbars Thermal Parameters
- Min: -50°C / Max: Extended +130°C
- Cooling system: Natural convection
- Relative humidity: Max: 55°C / 95% RH
- Storage temperature range: Min: -50°C / Max: +85°C
- Ambient temperature range: Min: -50°C / Max: Standard +105°C
ROLINX Busbars Applications


Conclusion
Rolinx Busbars considered a technological paradigm shift in electrical power distribution
In the dynamic landscape of electrical engineering, Rolinx busbars represent a transformative leap beyond traditional power distribution technologies. These advanced electrical components embody the convergence of materials science, precision engineering, and innovative design, addressing critical challenges in modern electrical infrastructure. Thus, Rolinx busbars deliver unprecedented performance capabilities across diverse technological domains by integrating sophisticated multi-layered architectures and advanced thermal management techniques. The precision-engineered layering provides superior electromagnetic interference suppression, optimizes current transmission, and ensures consistent performance under challenging operational conditions. From electric vehicle power systems to renewable energy infrastructure, these busbars are not merely components but fundamental enablers of technological innovation.
The strategic significance of Rolinx busbars extends beyond their immediate technical capabilities. They represent a critical pathway toward next-generation electrical systems, offering organizations a means to optimize electrical performance, reduce system complexity, and enhance overall technological reliability. For this reason, by bridging advanced materials science with practical engineering principles, these busbars exemplify the continuous innovation required to meet increasingly complex electrical engineering challenges. In conclusion, as industries demand more sophisticated and efficient power distribution solutions, Rolinx busbars stand at the forefront of technological evolution, demonstrating the transformative potential of precision engineering and cutting-edge design in addressing the most demanding electrical infrastructure requirements.
Looking for aSolution?
Our Technical Experts are Here to Bring your VISION to Life. Let’s DISCUSS How Our SOLUTIONS Can Maximize the VALUE of your PROJECT





